Használati útmutató AVM FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE International
Olvassa el alább 📖 a magyar nyelvű használati útmutatót AVM FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE International (165 oldal) a router kategóriában. Ezt az útmutatót 5 ember találta hasznosnak és 2 felhasználó értékelte átlagosan 4.5 csillagra
Oldal 1/165

FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE
Configuration
and Operation
Configuratio
n
and O
p
eration

2
Table of Contents
Symbols and Highlighting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1 Getting to Know FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.1 FRITZ!Box at a Glance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2 LTE: Radio Standard for Connecting to the Internet. . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.3 Ports and Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
1.4 Buttons. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
1.5 LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2 Before You Connect the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.1 Contents of the FRITZ!Box Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.2 Requirements for Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.3 Security and Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3 Connecting FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1 Screwing On the LTE Antennae . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.2 Inserting the SIM Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
3.3 Connecting to Electrical Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4 Connecting the Computer to the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.1 Connecting Computers to the LAN Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.2 Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5 The FRITZ!Box User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.1 Opening the User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.2 Protecting the User Interface with a Password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.3 Saving the FRITZ!Box Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
6 Configuring an Internet Connection into
the LTE Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33

3
7 Connecting Telephony Devices to the FRITZ!Box. . . . . . 34
7.1 Connecting an Analog Telephony Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.2 Registering Cordless (DECT) Telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
7.3 Registering Smartphones with FRITZ!App Fon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
7.4 Connecting an IP Telephone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
8 Setting Up the FRITZ!Box for Telephone Calls . . . . . . . . 39
8.1 Entering Internet Telephone Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.2 Configuring Connected Telephones and Terminal Devices . . . . . . . 40
8.3 Making Telephone Calls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
9 Firmware Update: Updating the FRITZ!Box Software . . 42
10 FRITZ!Box as an Internet Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
10.1 Child Protection: Restricting Internet Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
10.2 Port Forwarding: Making Computers Accessible from the Internet. 44
10.3 Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
10.4 Remote Access over HTTPS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10.5 Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10.6 VPN: Remote Access to the Home Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
10.7 DNSSEC: Security for DNS Queries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
11 FRITZ!Box as a WLAN Base Station. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
11.1 Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
11.2 Guest Access: WLAN Connection for Guests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
11.3 Setting Up Night Service for WLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
11.4 Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
11.5 WLAN Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
11.6 Frequency Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62

4
12 FRITZ!Box as a Telephone System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
12.1 Using the Telephone Book and Call List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
12.2 Setting Up the FRITZ!Box Answering Machine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
12.3 Setting Up FRITZ!Box Fax Reception . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
12.4 Setting Up Call Diversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
12.5 Saving Costs with Dialing Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12.6 Blocking Telephone Numbers and Callers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12.7 Setting Up Do Not Disturb . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
12.8 Setting Up the Alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
12.9 Enabling the Baby Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
12.10 Making Telephone Calls with Convenience Functions. . . . . . . . . . . 75
13 FRITZ!Box as a DECT Base Station . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
13.1 Paging Cordless Telephones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
13.2 Deregistering a Cordless Telephone from the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . 83
13.3 Enabling DECT Eco . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
14 The FRITZ!Box Home Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
15 Network Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network . . . . 87
15.1 Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
15.2 Obtaining an IP Address Automatically . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
16 USB Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network . . . . . . . . 97
16.1 Power Supply for USB Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
16.2 USB Devices on the FRITZ!Box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
16.3 Using USB Devices Safely . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
16.4 Accessing USB Memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
16.5 Sharing a USB Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
17 Saving Energy with FRITZ!Box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
17.1 Saving Energy with the WLAN Radio Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
17.2 Enabling Energy-saving Mode for USB Hard Drives . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
17.3 Saving Energy at the LAN Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107

5
18 Help in Case of Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
18.1 The User Interface Does Not Open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
18.2 Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
19 Configuring FRITZ!Box on the Telephone . . . . . . . . . . . 120
19.1 Restoring Factory Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
19.2 Switching WLAN On and Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
19.3 Turning Do Not Disturb On/Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
19.4 Switching the Alarm On and Off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
19.5 Setting Up Call Diversion. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
19.6 Disabling Automatic Outside Dialing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
20 Taking FRITZ!Box out of Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
20.1 Removing the SIM Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
20.2 Restoring the FRITZ!Box Factory Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
20.3 Uninstalling Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
21 Technical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
21.1 Ports and Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
21.2 Router Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
21.3 User Interface and Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
21.4 Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
21.5 Cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
22 Customer Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
22.1 Documentation on the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
22.2 Information in the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
22.3 Support from the Support Team . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
23 AVM Products for the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Legal Notice. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Legal Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Declaration of CE Conformity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Disposal Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143

6
Drilling Template. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Glossary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
7
Symbols and Highlighting
Symbols and emphasized text are used to mark certain information in
this manual.
Symbols
Highlighting
This symbol designates hints and tips that are useful in oper-
ating your product.
This symbol indicates important instructions that must be
observed to avoid malfunctions.
Highlighting Function Examples
Quotation marks Keys
Buttons
Menus
File paths
Folder and file
names
“F1” key
“Help”
“Home Network”
“C:\My Documents”
“Documentation”
Pointed brackets Joker <Telephone number>
Blue and under-
lined
Address to be en-
tered in the web
browser
fritz.box
Blue text links and references
within this manual
For more information on
customer service, see
the section from
page 132.
Bold Emphasis Do not click the button ...

8
Getting to Know FRITZ!Box
1 Getting to Know FRITZ!Box
This chapter gives you an overview of the features and functions of
your FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE and describes ports, buttons and LEDs.
1.1 FRITZ!Box at a Glance
Access to the Internet
The FRITZ!Box connects multiple computers fast and safely
with the Internet. Other network-compatible devices like
smartphones and game consoles can use the FRITZ!Box for
their Internet connection.
For fast Internet connections via the LTE radio standard, an
LTE modem is integrated into the FRITZ!Box. A preconfigured
firewall protects your network from attacks from the Internet.
The FRITZ!Box also offers a variety of functions to control ac-
cess to the Internet as well as access from the Internet. The
“Internet filter” feature allows you to restrict access to the In-
ternet for individual Windows users or computers, for in-
stance for you children’s computers. With the integrated VPN
server you can link remote computers securely with the home
network of the FRITZ!Box over the Internet.
WLAN Base Station for Wireless Connections
Computers and other network devices that support WLAN can
be connected wirelessly with the FRITZ!Box. If no WLAN de-
vice is integrated in your computer, you can install an external
WLAN adapter like a FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick by AVM (see also
AVM Products for the FRITZ!Box from page 135).
The FRITZ!Box supports the fast WLAN N standard, which pro-
vides for data throughput of up to 300 Mbit/s (gross).
You can use the FRITZ!Box in either the 2.4-GHz frequency
band or the 5-GHz frequency band (dual band). Because the
5-GHz frequency band is used less frequently, connections in
this band are subject to less interference.
With the “guest access” feature you can grant friends and vis-
itors fast, secure access to the Internet over your wireless net-
work.

FRITZ!Box at a Glance
9
Telephone System (PBX)
The FRITZ!Box is a telephone system (or PBX: private branch
exchange) for the Internet telephone line.
The PBX is also equipped with up to five integrated answering
machines and one integrated fax machine for fax reception.
You do not need any more additional devices for these func-
tions. For up to five different telephone numbers in the
FRITZ!Box you can configure a separate answering machine.
The FRITZ!Box can be configured to forward new messages on
an answering machine and new faxes automatically by e-
mail.
The FRITZ!Box telephone book is easy to manage in the web
browser. If you use multiple FRITZ!Box cordless telephones on
the FRITZ!Fon, you can use a shared telephone book or set up
a separate telephone book for each FRITZ!Fon in the
FRITZ!Box.
In addition, the FRITZ!Box telephone functions offer conve-
nience features like a call list, call diversion and do not Dis-
turbDo Not Disturb.
DECT Base Station for Cordless Telephones
A DECT base station is integrated in your FRITZ!Box. Up to six
cordless telephones can be connected with the FRITZ!Box:
you do not need an additional base station.
You can use the FRITZ!Box as a DECT base station or as a re-
peater. When used as a repeater, the FRITZ!Box increases the
range of another FRITZ!Box’s DECT radio network.
Switchboard in the Home Network
The FRITZ!Box connects your computers and other network
devices not only with the Internet, but also with each other.
The connected network devices constitute the home network
of the FRITZ!Box and can exchange data among each other.
You connect computers and other network devices with the
FRITZ!Box either wirelessly via WLAN or using a network ca-
ble.

10
LTE: Radio Standard for Connecting to the Internet
The FRITZ!Box can manage various storage media and make
them available to all participants in the home network. These
include connected USB flash drives, USB hard drives and on-
line storage.
USB 2.0 Port
The FRITZ!Box has a USB port which can be used to integrate
USB devices into your home network, for instance a printer or
a storage medium. The connected USB devices can then be
used simultaneously by all network devices in the home net-
work of the FRITZ!Box.
Media Server for Music, Images, and Video in the Home
Network
As a media server the FRITZ!Box makes music, video and im-
age files available throughout the entire home network. With
suitable playback devices in the home network of the
FRITZ!Box you can even play back the media files when the
computer is turned off.
Your music, video and image files can be stored on a USB
storage medium connected to the FRITZ!Box.
The playback devices or programs, for instance computers or
television sets, must support the UPnP AV or DLNA standard.
1.2 LTE: Radio Standard for Connecting to the Internet
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is a radio standard specified ac-
cording to the 3GPP standard, Release 8 . Within this stan-
dard the FRITZ!Box belongs to category 3 UE (user equip-
ment).
Frequency Ranges
LTE supports two frequency bands:
•791 - 862 MHz: the LTE band 20 is located in this range.
This band is called the “digital dividend” spectrum.
•2500 - 2690 MHz: the LTE band 7 is located in this range.
Ports and Interfaces
11
Channel Bandwidth
Within these two frequency bands the FRITZ!Box supports the
channel bandwidths 5, 10 and 20 MHz.
The smaller the channel bandwidth, the lower the throughput:
All devices located in the same radio cell share the band-
width and thus the throughput.
Antenna Technology
The FRITZ!Box supports Multiple-In-Multiple-Out (MIMO) an-
tenna technology.
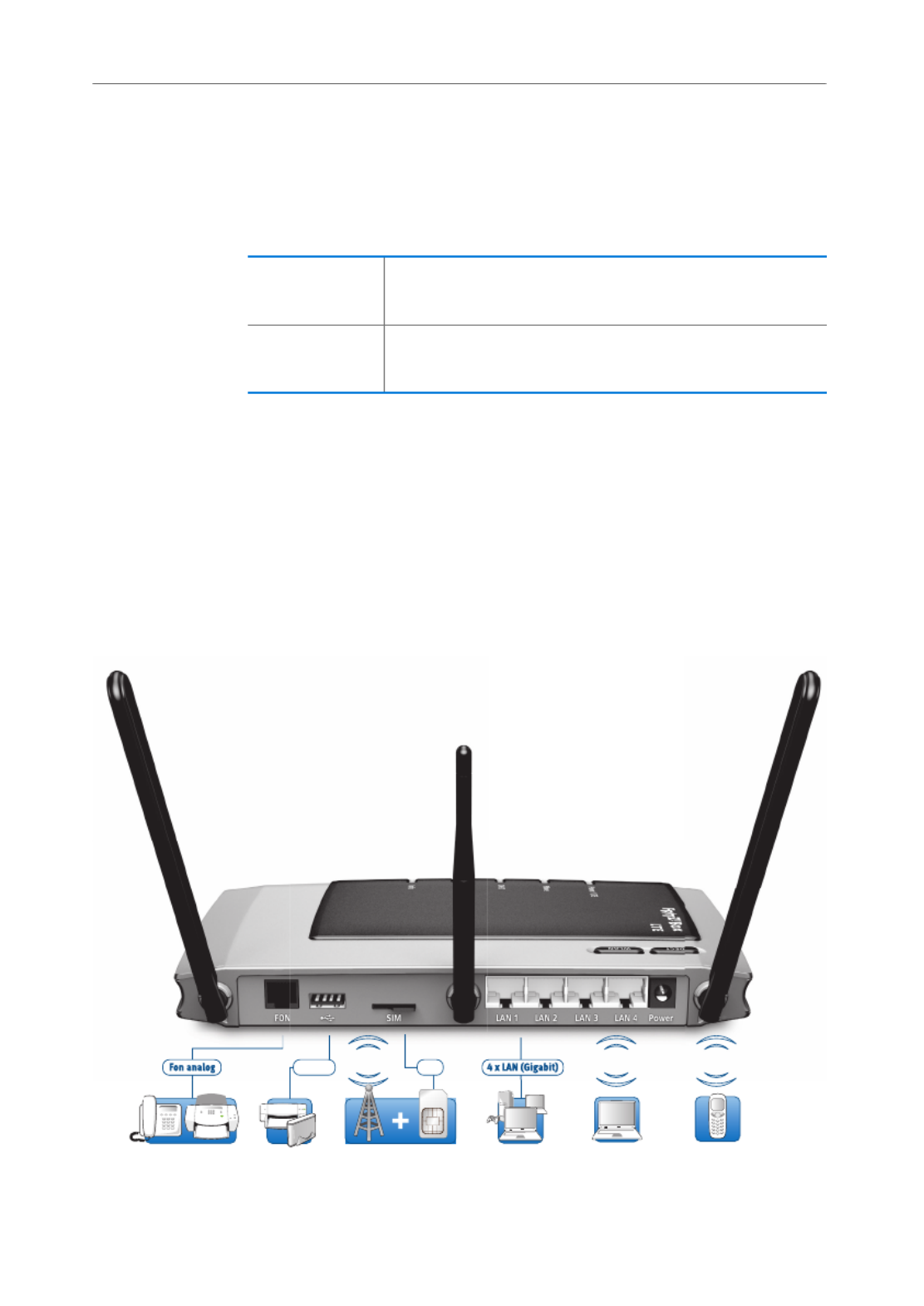
1.3 Ports and Interfaces
Possibilities for connecting the FRITZ!Box
20 MHz up to 100 Mbit/s download
up to 50 Mbit/s upload
10 MHz up to 60 Mbit/s download
up to 38 Mbit/s upload
Computer, game
console, network
Analog telephone,
fax
4 x LAN (Gigabit)
Notebook, smartphone,
video/TV Streaming
Fon analog
Printer,
storage media
USB 2.0
FRITZ!Fon or other
DECT telephones
DECT
LTE SIM card
SIM
WLANLT E

12
Buttons
•FON
One RJ11 socket for one analog telephone or another an-
alog terminal device
•LAN 1 – LAN 4
4 gigabit Ethernet ports (10/100/1000 Base-T) for con-
necting computers and other network devices like game
consoles and network hubs
•USB
USB 2.0 port for connecting USB devices like printers or
storage media
•WLAN base station
Integrated WLAN base station for connecting to WLAN
devices that use the radio standard IEEE 802.11a,
IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g or IEEE 802.11n (in the 2.4-
or 5-GHz frequency band)
•DECT base station
Integrated DECT base station for connecting up to
6 cordless telephones that use the DECT standard
1.4 Buttons
The FRITZ!Box has two buttons on the upper side of the hous-
ing.
FRITZ!Box buttons
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Powe
Powe
Powe
Powe
Power
r
r
r
r/
/
/
/
/ LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
Info
Info
Info
Info
Info

LEDs
13
WLAN Button
With the WLAN button you can turn the WLAN function on and
off and connect wireless devices with the FRITZ!Box by WPS.
WPS is an easy way to establish secure wireless connections
(see page 25).
DECT Button
With the DECT button you can register cordless telephones on
the FRITZ!Box (see page 34) and page misplaced cordless
handsets (see page 83).
1.5 LEDs
LED Condition Meaning
Power /
LTE
on •FRITZ!Box on standby
•Device has electrical power and the LTE connection has
been established
flashing •Device has electrical power
•LTE connection is being established or has been inter-
rupted
Phone on Telephone connection to the Internet active
flashing Messages in your voicemail/e-mail inbox (this function
must be supported by your telephony provider)
DECT on DECT function enabled
flashing Registration procedure for a DECT handset in progress
WLAN on WLAN function enabled
flashing •Enabling or disabling WLAN function
•Adopting the WLAN settings

14
LEDs
Info LED
Here you can define what additional information should be
displayed on the “Info” LED. For details, see the “System / In-
fo Display” section of the user interface of your FRITZ!Box
6840 LTE.
Info on •Telephone connection between two Internet telephony
subscribers is active; the call is free of charge (this func-
tion must be supported by your Internet telephony pro-
vider)
•Signals an event specified by the user
flashing •Updating the firmware
•Specified value for online meter reached
•Signals an event specified by the user
flashing red Error: Open the FRITZ!Box user interface and follow the in-
structions on the “Overview” page
LED Condition Meaning

Before You Connect the FRITZ!Box
15
2 Before You Connect the FRITZ!Box
•Check the contents of your FRITZ!Box package. See the section
Contents of the FRITZ!Box Package on page 15 for more informa-
tion.
•Make sure that the requirements for connecting and operating
the FRITZ!Box have been met. See the section Requirements for
Operation on page 15 for more information.
•Please see the security and handling instructions in the section
Security and Handling on page 16.
2.1 Contents of the FRITZ!Box Package
•FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE
•two LTE antennae
•one power supply unit
•one network cable
•a FRITZ!Box CD with the FRITZ!Box manual as a PDF file
•printed product information
2.2 Requirements for Operation
In order to operate the FRITZ!Box, you must have the follow-
ing:
•a web browser that supports Java script (for instance, In-
ternet Explorer version 8.0 or higher, or Firefox version 7
or higher)
•an LTE SIM card for the Internet connection
•for connecting computers via WLAN:
computer with WLAN support (compliant with
IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11a or
IEEE 802.11b). Computers that do not have integrated
WLAN can be equipped with WLAN support by installing
a WLAN device like a FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick N, for in-
stance.

16
Security and Handling
•for connecting computers using network cable:
computer with a network port (network adapter standard
Ethernet 10/100/1000 Base-T)
2.3 Security and Handling
Before installing and using the FRITZ!Box, please read the fol-
lowing security and handling instructions.
Safety Instructions
•Before mounting the FRITZ!Box on the wall, make sure
that there are no electrical lines, gas or water pipes lo-
cated where you need to drill the holes.
If necessary, check the site it with a pipe detector or con-
sult with qualified experts.
•Do not place FRITZ!Box on excessively heat-sensitive sur-
faces, as the base of the device can heat up during nor-
mal operation.
•Make sure that the ventilation slits on the FRITZ!Box
housing are always unobstructed. The ventilation slits
provide for air cooling.
–The FRITZ!Box should not be placed on a carpet or on
upholstered furniture.
–Do not cover the FRITZ!Box.
•Do not install the FRITZ!Box during an electrical storm.
•Disconnect the FRITZ!Box from the power supply during
electrical storms.
•Never let liquids get inside the FRITZ!Box. Otherwise,
electric shocks or short circuits may result.
•The FRITZ!Box is intended for indoor use only.
When working with the FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE, be sure to ob-
serve the following security instructions in order to protect
yourself and the FRITZ!Box from harm.

Security and Handling
17
•Do not open the FRITZ!Box housing. The device contains
hazardous components and should only be opened by
authorized repair technicians.
Handling the FRITZ!Box
•You can either place FRITZ!Box on a horizontal surface or
mount it on a wall. For a drilling template to mount the
FRITZ!Box on a wall, see page 144.
•Place or hang the FRITZ!Box in a dry location that is free
of dust and protected from direct sunlight.
•For ideal operating conditions, mount the FRITZ!Box on a
wall with the cables connected on the bottom.
•When connecting FRITZ!Box to your computer using a
network cable, keep in mind that the cable can be no
longer than 100 m.
•If you would like to establish wireless connections be-
tween the FRITZ!Box and the computer, position the
FRITZ!Box at a central location.
•Make sure to keep sufficient distance from potential
sources of interference like microwave devices or elec-
tric devices with large metal housings.

18
Connecting FRITZ!Box
3 Connecting FRITZ!Box
•Screw the LTE antennae onto the FRITZ!Box and insert the SIM
card.
•Connect the FRITZ!Box to the power supply.
This chapter tells you how.
3.1 Screwing On the LTE Antennae
Screwing On the LTE Antennae
1. Pick up the two LTE antennae included in the package.
2. Screw the antennae onto the sockets labeled “LTE”.
Connecting Exterior Antenna
You can also connect the FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE with an exterior
antenna rather than using the LTE antennae included with de-
livery. If areas located on the edge of LTE radio coverage, the
two LTE included in the package may not be sufficient for suc-
cessful radio traffic. If this is the case, you can use a stronger
antenna, for instance, one mounted on your roof.
Before you connect the FRITZ!Box, note the additional in-
structions in the section Security and Handling on page 16.
SIMSIM LT ELT E
LT ELT E

Inserting the SIM Card
19
Please note the following if you would like to use an exterior
antenna:
•The antenna has to fit into an SMA socket. The antenna
sockets on the FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE are SMA connectors.
•The plugs on the antenna cable used to connect the
FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE and the antenna must be SMA plugs.
•The FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE receives on both antenna sock-
ets and transmits on only one. The antenna socket on
the left of the FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE socket panel ist the
one for transmission:
If your exterior antenna has only one connector, connect
the antenna to this antenna socket and screw one of the
LTE antennae included with delivery into the other an-
tenna socket.
If the exterior antenna has two connectors, connect the
antenna to both antenna sockets on the FRITZ!Box 6840
LTE.
3.2 Inserting the SIM Card
You received a SIM card from your LTE provider. This card
must be inserted into the card holder in the FRITZ!Box SIM
card slot.
SIMSIM
LT ELT E

20
Connecting to Electrical Power
1. Pull the card holder completely out of the SIM card slot.
2. Place the SIM card with the slanted edge in the bottom
right corner with the contacts facing downwards.
3. Insert the card holder with the SIM card back into the
SIM card slot.
3.3 Connecting to Electrical Power
Connecting to the power supply
1. Pick up the power supply unit included in the FRITZ!Box
package.
2. Connect the power supply unit to the socket on the
FRITZ!Box labeled “Power”.
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
Info
Info
Info
Info
Info
SIM
SIM
SIM
SIM
SIM
SIM-Karte
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
Info
Info
Info
Info
Info
SIM
SIM
SIM
SIM
SIM
SIM-Karte
1 2 3
DECT
WLAN
Info
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
SIMSIM LT ELT E
LT ELT E
WLAN
Use only this power supply unit for connecting to electri-
cal power.

Connecting to Electrical Power
21
3. Plug the other end into an AC power outlet.
The “Power / LTE” LED begins flashing after a few seconds to
indicate that the LTE connection is being established.

22
Connecting the Computer to the FRITZ!Box
4 Connecting the Computer to the FRITZ!Box
Connect one or several computers to the FRITZ!Box.
4.1 Connecting Computers to the LAN Port
Connecting a computer to a LAN port on the FRITZ!Box
1. Set aside the network cable (yellow) from the FRITZ!Box
package.
2. If you work with a Linux operating system: Configure the
network adapter of the computer with the setting
“DHCP”.
3. Connect one end of the network cable to the network
port (network card) of the computer.
4. Connect the other end to the “LAN 1”, “LAN 2”, “LAN 3”
or “LAN 4” socket on the FRITZ!Box.
SIMSIM LT ELT E
LT ELT E

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
23
Now the FRITZ!Box and the computer are connected to each
other.
Connecting More Computers to the LAN Ports
Additional cables are required to connect further computers.
In purchasing a LAN cable, note the instructions in the sec-
tion Network Cable on page 131.
One computer can be connected to each network port of the
FRITZ!Box.
Connecting a Network Hub or Switch
You can also connect a network hub or switch to the LAN
ports on the FRITZ!Box.
Connecting FRITZ!Box to a network hub
1. Set aside the network cable (yellow) from the FRITZ!Box
package.
2. Connect one end of the LAN cable to the uplink port (see
glossary) of the network hub or network switch.
3. Connect the other end of the cable to one of the LAN
ports on the FRITZ!Box.
The FRITZ!Box and the network hub are now connected with
each other.
4.2 Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
Using WLAN radio technology you can connect multiple com-
puters with the FRITZ!Box wirelessly.
SIMSIM LTELTE
LTELTE

24
Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
Please note the following before establishing a wireless con-
nection between the computer and the FRITZ!Box:
•WLAN device
A computer to be connected to the FRITZ!Box via WLAN
must be equipped with a WLAN device for it to support
WLAN. A WLAN device can be an external WLAN adap-
ter—like a USB stick, for example—or a device integrated
in the computer. Many modern computers and note-
books come with a WLAN device integrated.
•WLAN security settings
In the FRITZ!Box, WLAN security settings are enabled up-
on delivery. Before a computer can establish a wireless
connection to the FRITZ!Box, the WLAN security settings
of the FRITZ!Box must be transferred to the WLAN device.
For this procedure the FRITZ!Box supports the two auto-
matic methods AVM Stick & Surf and WPS (Wi-Fi Protect-
ed Setup). The security settings can also be transferred
manually.
For more information on WLAN, see the section FRITZ!Box as
a WLAN Base Station from page 52.

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
25
Establishing a WLAN Connection with AVM Stick & Surf
If you use a FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick from AVM as the WLAN de-
vice, you can use AVM Stick & Surf to establish a secure
WLAN connection quickly and conveniently.
1. Switch on your computer.
2. Insert the your FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick into the USB port
on the FRITZ!Box.
The WLAN security settings are transmitted to the
FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick. The “Info” LED on the FRITZ!Box
begins flashing quickly.
As soon as the “Info” LED stops flashing, transmission
of the settings has been concluded.
3. Remove the FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick.
4. Now insert the FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick into the USB port
of the computer.
The security settings will be adopted and the WLAN connec-
tion between the FRITZ!Box and the FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick
will be established. As soon as the WLAN connection has
been established the computer is connected to the FRITZ!Box.
Establishing a WLAN Connection Using WPS
The FRITZ!Box supports WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). WLAN
devices that also support WPS can be connected with your
FRITZ!Box securely using this method. All of the necessary
WLAN security settings are transferred in the process. There
are two kinds of WPS: the push-button method and the PIN
method.
See the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick manual for details.

26
Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
WPS with the Push-button Method
The push-button method (WPS PBC) can be used if your WLAN
device is also equipped with a WPS button, or if WPS can be
enabled via the control software of the WLAN device.
1. Press the “WLAN” button on the FRITZ!Box and hold it
down for at least six seconds.
2. As soon as the “WLAN” LED begins flashing, enable the
WPS function on the other WLAN device, either by press-
ing a button or in the device’s user interface (depending
on the device). Activation must be started within
two minutes.
The FRITZ!Box and the WLAN device now connect with each
other automatically. The WLAN device adopts the security set-
tings of the FRITZ!Box.
As soon as the WLAN connection has been established the
computer is connected to the FRITZ!Box.
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Powe
Powe
Powe
Powe
Power
r
r
r
r/
/
/
/
/ LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
Info
Info
Info
Info
Info

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
27
WPS with the PIN Method
If your WLAN device supports WPS, but does not have a but-
ton to start the push method nor any possibility to enable it in
its control software, use the PIN method to establish the
WLAN connection.
You can choose between two methods:
•the FRITZ!Box specifies the PIN
•the WLAN device specifies the PIN.
The FRITZ!Box Specifies the PIN
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Select the “WLAN / Security” menu.
3. Go to the “WPS / Quick Connection”page.
4. Enable the setting “WPS enabled”.
5. Select the option “PIN method (WPS-PIN), the FRITZ!Box
specifies the PIN”.
6. The PIN will be displayed. Enter this PIN in the control
software of the WLAN device.
7. Click “Start WPS”.
The “WLAN” LED on the FRITZ!Box flashes slowly, indicating
that the WPS procedure has begun. Now a secure WLAN con-
nection is being established between the FRITZ!Box and the
WLAN device.
The WLAN Device Specifies the PIN
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Select the “WLAN / Security” menu.
3. Go to the “WPS / Quick Connection”page.
4. Enable the setting “WPS enabled”.
5. Select the option “PIN method (WPS-PIN), the WLAN de-
vice specifies the PIN”.

28
Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
6. Now start the control software of the WLAN device. The
program outputs a PIN for establishing a connection.
7. Enter this PIN in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
8. Click “Start WPS”.
The “WLAN” LED on the FRITZ!Box flashes slowly, indicating
that the WPS procedure has begun. Now a secure WLAN con-
nection is being established between the FRITZ!Box and the
WLAN device.
Transferring the WLAN Security Settings Manually
The WLAN security settings for WLAN devices can also be
transferred manually. Manual transfer is unavoidable if a
WLAN device does not support any methods for transferring
the security settings automatically.
For manual transfer the WLAN security settings have to be en-
tered in the WLAN software.
WLAN devices are generally delivered with their own WLAN
software, which is installed in the computer along with the
WLAN device. By now many operating systems have WLAN
software included. Integrated WLAN devices sometimes use
the operating system’s WLAN software.
Installing a WLAN Device
If you need to use a separate WLAN device because you do
not have one integrated, then install the WLAN device in the
computer along with the corresponding WLAN software.
Please take note of the instructions in the documentation of
the device.

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
29
Transferring WLAN Security Settings
The values for WLAN security preconfigured in the FRITZ!Box
have to be transferred to the WLAN device.
1. Start the WLAN software.
2. Enter the following values for the connection between
the FRITZ!Box and the WLAN device:
3. Confirm your entries using the relevant button in the us-
er interface (for instance, “OK” or “Connect”).
Now your WLAN device and the FRITZ!Box are connected with
each other wirelessly.
If you would like to establish a WLAN connection using the
values preset in the FRITZ!Box, then your WLAN device must
support the WPA encryption procedure.
SSID (name of the
WLAN radio net-
work)
FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE
Encryption method WPA (TKIP) or WPA2 (AES-CCMP)
Encryption WPA PSK or WPA2 PSK (AES)
WLAN key The key is printed on the sticker on the
bottom of the housing and on the cover
of the FRITZ!Box CD.
Network mode Infrastructure

30
The FRITZ!Box User Interface
5 The FRITZ!Box User Interface
The FRITZ!Box has a user interface you can open in a web browser on
your computer.
In the user interface you can set up the FRITZ!Box, enable or disable
functions and receive information on the FRITZ!Box and on your con-
nections.
5.1 Opening the User Interface
The FRITZ!Box user interface can be opened on every comput-
er connected with the FRITZ!Box.
1. Start a web browser on your computer.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address line of the browser.
The FRITZ!Box user interface opens.
Entering the address fritz.box in the browser
The Wizard: Opening the User Interface for the First Time
When you open the user interface for the first time, a wizard
starts to assist you in configuring the FRITZ!Box.
If you cancel the wizard, you can configure your FRITZ!Box
without this wizard. You can change the settings configured
with this wizard at any time.
For comprehensive information on configuring the many di-
verse functions of your FRITZ!Box, see the following chapters
in this manual.
If the user interface does not open, see the instructions on
resolving errors in the section from page 108.

Protecting the User Interface with a Password
31
5.2 Protecting the User Interface with a Password
You can protect the user interface of the FRITZ!Box with a
password. The password will be requested every time the us-
er interface is opened. This protects the settings of your
FRITZ!Box from unauthorized access.
Setting Up Password Protection
As long as no password protection has been set up, every
time you open the user interface you will be prompted to en-
ter a password. If you disabled this message, here is how to
set password protection:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Go to the “System / FRITZ!Box Password” menu.
3. Enter a password and save the password by clicking
“Apply”.
Password protection is now enabled.
Logging Off the User Interface
When password protection is enabled, you can log off the us-
er interface at any time. To do so, click .
If you do not click on the user interface for a period of longer
than ten minutes, you will be logged off automatically. The
only pages excepted from this are those which are constantly
updated, like the “Overview” page. No automatic logout will
take place on these pages.
We strongly recommend setting up and using password pro-
tection for the user interface.
Be sure to remember the password! If you forget the pass-
word, the factory settings will have to be restored to your
FRITZ!Box (see page 128). All of the settings you configured
will be discarded.

32
Saving the FRITZ!Box Settings
5.3 Saving the FRITZ!Box Settings
All of the settings you configure in your FRITZ!Box can be
saved in a backup file on your computer. With this backup file
you can restore your settings to the FRITZ!Box at any time or
load your settings to another FRITZ!Box.
Saving and Restoring Settings
To save and restore your FRITZ!Box settings, use the “System
/ Save Settings” menu in the user interface. Here you can
•save your FRITZ!Box settings on the “Save” tab.
•restore all of your saved settings to the same FRITZ!Box
on the “Restore” tab.
•load all of your saved settings to another FRITZ!Box of
the same model on the “Restore” tab.
•load your saved settings to another FRITZ!Box model on
the “Apply” tab. In this case you can select which set-
tings are to be applied to the FRITZ!Box.
Instructions for saving, restoring and applying FRITZ!Box files
are presented in the user interface’s Online Help.
To load your saved settings to another FRITZ!Box of the same
model, or to apply your FRITZ!Box settings to another
FRITZ!Box model, the backup file must always be password
protected.

Configuring an Internet Connection into the LTE Network
33
6 Configuring an Internet Connection into the LTE
Network
The Internet connection for the mobile telephone network has
to be set up once in the FRITZ!Box, then it is always available.
Along with the SIM card you received a PIN (Personal Identifi-
cation Number) and a corresponding PUK (Personal Unlock
Key) from your mobile telephone network provider. Keep both
numbers handy.
The first time you open the FRITZ!Box user interface, you will
automatically be prompted to configure the Internet connec-
tion.
1. Start a web browser on your computer.
2. Enter fritz.box in the address field of the web browser.
3. The Wizard for configuring the Internet connection starts
automatically.
4. Follow the instructions displayed on the screen.
5. As soon as you are prompted to do so, enter the PIN. If
you enter the PIN incorrectly during login three times in a
row, the device is blocked for further entries. With the
PUK you can release this block.

34
Connecting Telephony Devices to the FRITZ!Box
7 Connecting Telephony Devices to the FRITZ!Box
This chapter describes how to connect telephones, fax machines, an-
swering machines and telephone systems to the FRITZ!Box.
7.1 Connecting an Analog Telephony Device
You can connect an analog telephone, an analog fax machine
or an analog answering machine to the FRITZ!Box.
Connecting an analog telephone with an RJ11 plug
Connect the telephone device to the “FON” port of the
FRITZ!Box.
7.2 Registering Cordless (DECT) Telephones
Up to six cordless telephones that support the DECT standard
can be registered on the FRITZ!Box.
Registering FRITZ!Fon Cordless Telephones
The cordless telephones FRITZ!Fon by AVM are the ideal com-
plement to your FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE (see also AVM Products
for the FRITZ!Box from page 135).
SIMSIM LT ELT E
LT E
LT E
For instructions on how to set up the FRITZ!Box for making
telephone calls, start reading from page 39.

Registering Cordless (DECT) Telephones
35
Connecting a cordless telephone
Here is how to register your FRITZ!Fon on the FRITZ!Box:
1. Switch your FRITZ!Fon on by pressing and holding down
the hang-up button.
2. Press and hold down the “DECT” button on the
FRITZ!Box. Hold the button down until the “DECT” LED on
the FRITZ!Box begins flashing.
Your FRITZ!Fon will be registered at the FRITZ!Box.
If registration fails, register the FRITZ!Fon on the FRITZ!Box
manually as described in the following section.
Registering Any DECT Cordless Telephone
1. Start the process of registering your cordless telephone
at a base station and follow the instructions.
2. As soon as you are prompted to press the registration
button on the base station, press the “DECT” button on
the FRITZ!Box and hold it down until the “DECT” LED on
the FRITZ!Box begins flashing.
DECT
Registering...
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Powe
Powe
Powe
Powe
Power
r
r
r
r/
/
/
/
/ LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
Info
Info
Info
Info
Info
10 seconds
Upon delivery of the FRITZ!Box, the PIN for the integrat-
ed DECT base station is set to “0000”.

36
Registering Smartphones with FRITZ!App Fon
7.3 Registering Smartphones with FRITZ!App Fon
The FRITZ!App Fon software connects your smartphone with
the FRITZ!Box via WLAN. Calls you make from home then use
not the mobile telephone network, but the telephone num-
bers set up in the FRITZ!Box.
The free FRITZ!App Fon software can be installed on an iP-
hone, iPod or iPad with iOS4 or higher, and on Android smart-
phones with Google Android 2.1 or higher.
FRITZ!App Fon for Android smartphones is available at the
Android Market. FRITZ!App Fon for iOS is offered in the Apple
App Store.
Registering a Smartphone on FRITZ!Box
1. Install FRITZ!App Fon on your smartphone.
2. Connect your smartphone with the FRITZ!Box via WLAN.
To establish the connection you need the WLAN key of
the FRITZ!Box. The preconfigured WLAN key is printed on
the sticker on the underside of the FRITZ!Box and on the
FRITZ!Box CD jewel case.
3. Start the FRITZ!App Fon. If you protected the user inter-
face of the FRITZ!Box with a password, enter the pass-
word to log in.
Once FRITZ!App Fon has been started, use your smartphone
to make calls from home over the FRITZ!Box.
Defining Telephone Numbers for the Smartphone
A new telephone device for FRITZ!App Fon is entered automat-
ically in the FRITZ!Box. The name of the telephone device is
listed in the FRITZ!App Fon under “More / FRITZ!Box”.
You can assign telephone numbers to this telephone to deter-
mine which telephone numbers are used to make calls with
your smartphone from home. See the section Configuring
Connected Telephones and Terminal Devices on page 40 for
instructions.

Connecting an IP Telephone
37
7.4 Connecting an IP Telephone
Connect an IP telephone by plugging it into a network port on
the FRITZ!Box or wirelessly via WLAN.
Connecting an IP Telephone to the LAN Port of the FRITZ!Box
IP telephones with a LAN port can be connected to the
FRITZ!Box with a network cable.
Connecting an IP telephone to the network port of the FRITZ!Box
1. Connect a network cable to the IP telephone.
2. Connect the free end of the network cable to a LAN port
on the FRITZ!Box.
The IP telephone is now connected with the FRITZ!Box.
SIMSIM LT ELT E
LT ELT E
You cannot make calls with the IP telephone yet. The IP tele-
phone still has to be configured in the FRITZ!Box (see
page 40).

38
Connecting an IP Telephone
Connecting an IP Telephone with the FRITZ!Box over WLAN
IP telephones that support WLAN can be connected wirelessly
to the FRITZ!Box via WLAN.
Connecting an IP telephone with the FRITZ!Box over WLAN
1. Use your IP telephone to search for WLAN devices at your
location.
2. Select your FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE from the list of WLAN de-
vices found.
3. Enter the WLAN key of the FRITZ!Box.
The preconfigured WLAN key is printed on the sticker on
the underside of the FRITZ!Box and on the FRITZ!Box CD
jewel case.
Now the IP telephone will be connected with the FRITZ!Box.
WLAN
SIM
SIM LT ELT E
LT ELT E
You cannot make calls with the IP telephone yet. The IP tele-
phone still has to be configured in the FRITZ!Box (see
page 40).

Setting Up the FRITZ!Box for Telephone Calls
39
8 Setting Up the FRITZ!Box for Telephone Calls
This chapter describes how to set up your FRITZ!Box for making tele-
phone calls.
8.1 Entering Internet Telephone Numbers
Enter all telephone numbers you would like to use to make
calls over the Internet in the FRITZ!Box.
Automatic Configuration of Telephone Numbers
Various Internet telephony providers offer automatic configu-
ration of the Internet telephone numbers. They then automat-
ically configure your Internet telephone numbers in the
FRITZ!Box once the FRITZ!Box has been connected. To start
automatic configuration, some providers require that you en-
ter a start code.
The FRITZ!Box receives the data for automatic configuration
(also called “remote configuration”) from an “Auto Configura-
tion Server” (ACS), which is made available in the Internet by
the Internet telephony provider.
After automatic configuration, your Internet telephone num-
bers will be listed in the “Telephony / Internet Telephony”
menu in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
Entering Internet Telephone Numbers with the Wizard
Internet telephone numbers that are not configured automati-
cally can be entered using the “Manage Your Own Phone
Numbers” Wizard in the FRITZ!Box. You can even enter multi-
ple Internet numbers from different Internet telephony pro-
viders.
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Click “Wizards”.
The account information for your Internet telephone num-
bers, like the user name and the password, are obtained
from your Internet telephony provider.

40
Configuring Connected Telephones and Terminal Devices
3. Click “Manage Your Own Phone Numbers”.
The next page presents an overview of all telephone
numbers that have already been entered.
4. Click “Enter New Telephone Number” to enter a new In-
ternet telephone number. Follow the wizard’s instruc-
tions.
The Internet telephone number is entered in the FRITZ!Box. An
overview of your Internet telephone numbers is presented in
the FRITZ!Box user interface in the “Telephony / Internet Tele-
phony” menu. Here you can edit or delete Internet telephone
numbers as needed.
8.2 Configuring Connected Telephones and Terminal Devices
Once you have entered your telephone numbers in the
FRITZ!Box, set up the connected telephones, telephone sys-
tems (PBXs), fax machines and answering machines in the
FRITZ!Box. During configuration you must define the follow-
ing, depending on the type of device:
•The telephone number the terminal device uses to place
outgoing calls to the public telephone network.
•Telephone numbers for accepting calls. A telephone can
be set to ring for all incoming calls or only for calls to cer-
tain telephone numbers.
•Internal name for the terminal device. This name will be
displayed, for instance, in the call list of the FRITZ!Box.
The “Manage Your Telephony Devices” Wizard assists you in
setting up the telephones and other terminal devices:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Click “Wizards” in the menu.
3. Click “Manage Your Telephony Devices”.
You are presented with an overview of all telephones
and terminal devices that have already been set up.

Making Telephone Calls
41
4. Now you can set up a new terminal device or open the
settings of a terminal device:
To set up a new terminal device, click “Configure New
Device” and follow the Wizard’s instructions.
Click the “Edit” button to open the settings of a ter-
minal device.
All configured telephones and other terminal devices are dis-
played in an overview in the FRITZ!Box user interface. This
overview is found in the “Telephony / Telephony Devices”
menu. Here you can edit the settings of terminal devices and
delete terminal devices.
8.3 Making Telephone Calls
Once you have set up your telephones, you can make outgo-
ing telephone calls to the public network and accept incom-
ing calls.
A telephone places outgoing calls using the telephone num-
ber you defined for outgoing calls while setting up the tele-
phone (see page 40).
For incoming calls a telephone reacts only to calls to those
telephone numbers you assigned to the telephone during set-
up (see page 40).

42
Firmware Update: Updating the FRITZ!Box Software
9 Firmware Update: Updating the FRITZ!Box Software
AVM provides free updates of the firmware for the FRITZ!Box. The firm-
ware is the software stored in the FRITZ!Box that controls all of the
FRITZ!Box functions.
Firmware updates contain further developments of existing FRITZ!Box
functions and often also introduce new functions for your FRITZ!Box.
Finding New Firmware and Transferring It to the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Click “Wizards” in the menu and start the “Update Firm-
ware” Wizard.
The Wizard checks whether new firmware is available for
your FRITZ!Box.
If the Wizard finds new firmware, it displays the version
number of the firmware. Click the link under the firm-
ware version to view information about further develop-
ments and new functions contained in the firmware up-
date. Read this information before starting the firmware
update.
3. To transfer new firmware to the FRITZ!Box, click “Start
Firmware Update Now”.
The firmware update begins and the “Info” LED on the
FRITZ!Box starts flashing.
The firmware update is complete when the “Info” LED stops
flashing.
Do not interrupt the power supply to the FRITZ!Box dur-
ing the firmware update!

FRITZ!Box as an Internet Router
43
10 FRITZ!Box as an Internet Router
The FRITZ!Box connects computers in your home network with the In-
ternet. This chapter explains the possibilities offered by using the
FRITZ!Box as an Internet router and how to take advantage of them.
10.1 Child Protection: Restricting Internet Access
The child protection feature allows you to define access rules
to the Internet for individual computers or Windows users.
These access rules may include restrictions of Internet access
time, filter lists and a list with blocked network applications:
•Restrict Internet access time: Using the time restriction
you can restrict the amount of time the user can surf the
web. You can define on which days of the week, at what
times of day, and for how long a computer or Windows
user is allowed to use the Internet connection.
•Block or permit web sites: you can use filter lists to de-
fine which Internet pages are allowed to be accessed
and to which access is blocked. For instance, you can
block all Internet pages the government has defined as
offensive or harmful to minors.
You can create both filter lists, the whitelist and the
blacklist. A whitelist contains all Internet pages to which
access is allowed. A blacklist contains all Internet pages
to which access is blocked.
•Block network applications: You can list network appli-
cations for which Internet access should be blocked. For
instance, you can block Internet access for file-sharing
software.
Child protection can be enabled for each computer individu-
ally, regardless of the computer’s operating system.
You can also enable child protection individually in all Win-
dows operating systems (Windows 7, Windows Vista and
Windows XP). This option is very beneficial if a computer is
used by multiple users.

44
Port Forwarding: Making Computers Accessible from the Internet
Setting Up Child Protection in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Select the “Internet / Filters” menu.
3. Set up the child protection feature, making use of the
Online Help in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
10.2 Port Forwarding: Making Computers Accessible from the
Internet
With default settings in the FRITZ!Box, programs on your com-
puter and LAN cannot be accessed from the Internet. For a
number of applications like online games and file sharing
software, you have to make your computer accessible for oth-
er Internet users. In order to grant controlled access to your
computer to other Internet users, you release certain ports for
incoming connections. The ports serve to distinguish be-
tween running applications on a computer that has only one
IP address.
Setting Up Port Forwarding in the FRITZ!Box
•Port Forwarding is set up in the “Internet / Permit Ac-
cess”menu.
•Port Forwarding for IPv6 is also set up in the “Internet /
Permit Access” menu, on the “IPv6” page. To see this
page, make sure you enabled the expert mode in the
“System / Expert Mode” menu.
Address for Accessing the FRITZ!Box
If you have enabled the ports for forwarding in the FRITZ!Box,
other users can access your computer at the IP address as-
signed to your FRITZ!Box by the Internet Service Provider. This
is a public IP address.
Here is how to determine the public IP address of the
FRITZ!Box:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Enable the expert settings in the “System / Expert
Mode” menu.

Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address
45
3. Open any Internet page in order to establish an Internet
connection.
4. The FRITZ!Box’s public IP address is displayed on the
“Overview” page in the “Connections” area.
10.3 Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address
Dynamic DNS is an Internet service that makes it possible for
the FRITZ!Box to remain accessible from the Internet at all
times under a fixed name, even though the public IP address
changes.
You must register with a dynamic DNS provider to use this
service. When you register, you agree on the fixed name (do-
main name) at which your FRITZ!Box should be accessible
from the Internet. You also define a user name and password.
Every time the IP address changes, the FRITZ!Box transmits
the new IP address to the dynamic DNS provider in the form of
an update request. Then the domain name is assigned to the
current IP address by the dynamic DNS provider.
Setting Up Dynamic DNS in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Select the “Internet / Permit Access” menu.
4. Select the “Dynamic DNS” page and set up dynamic
DNS. Consult the Online Help available in the FRITZ!Box
user interface for more information.
Every time the Internet connection is interrupted the Internet
Service Provider re-assigns the IP address. The IP address
may change in the process. Therefore it is a good idea to use
dynamic DNS so that the IP address can always be reached
under the same name. For more information, see the section
Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address on page 45.

46
Remote Access over HTTPS
10.4 Remote Access over HTTPS
With this function it is possible to access the user interface of
the FRITZ!Box from another location. With this feature you can
configure settings in the FRITZ!Box or perform a firmware up-
date using a computer that is not in your own network (LAN or
WLAN).
Setting Up Remote Access over HTTPS in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Select the “Internet / Permit Access” menu.
4. Select the “Remote Access” page and set up dynamic
DNS. For more information, see the Online Help.
10.5 Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access
Prioritization is a function you can use to specify that network
applications and network devices be treated with higher or
lower priority when they access the Internet connection. For
example, you may wish to ensure that applications like Inter-
net telephony, IPTV and video on demand are always treated
with higher priority than other applications. You can also
specify that file-sharing applications like eMule and BitTor-
rent always have to wait behind online games.
Network applications and network devices are assigned to
the categories using rules.
Categories for Prioritization
There are three categories for prioritization: “Real-time appli-
cations”, “Prioritized applications” and “Background appli-
cations”. The categories are explained below.
Real-time Applications
This category is suitable for applications with high demands
on transmission speed and reaction times (for example, Inter-
net telephony, IPTV, video on demand).

Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access
47
•Network applications of this category always have priori-
ty over other applications accessing the Internet at the
same time.
•When the Internet connection is working at full capacity,
the network packets of the applications of this category
will always be sent first. In this case data from network
applications assigned to other categories, like “Priori-
tized applications”, will be transmitted later.
•If multiple network applications are assigned to this cat-
egory, then they must share the available capacity.
•Whenever Internet telephony is included in this catego-
ry, this application always has the highest priority, even
over other real-time applications.
Prioritized Applications
This category is suitable for applications that require a fast re-
action time (for example, company access, terminal applica-
tions, games).
•For network applications prioritized in this category,
90% of the FRITZ!Box’s upload bandwidth is available,
as long as no application from the “Real-time applica-
tions” category requires bandwidth. The remaining 10%
of the upload bandwidth is available for applications
that are prioritized in lower categories or not prioritized
at all.
•If multiple network applications are assigned to the “Pri-
oritized applications” category, then they must share
the available capacity.
Background Applications
This category is suitable for applications that do not require
any high transmission speed and which are not time-critical
(for example, peer-to-peer services or automatic updates).
•Network applications assigned to this category are al-
ways treated with the lowest priority when the Internet
connection is working at full capacity. So whenever an
application from a different category or a non-prioritized

48
Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access
application requires the entire bandwidth, all back-
ground applications must wait until bandwidth capacity
becomes available again.
•If no other network applications are active, then the
background applications receive the entire bandwidth.
Prioritization Method in the FRITZ!Box
The following algorithm is used in the FRITZ!Box to send data
packets according to their prioritization:
•Change in the order in which packets are sent to the In-
ternet (upstream direction)
The order of the packets the FRITZ!Box receives from the
Internet (downstream direction) cannot be changed.
•Discard low-priority packets in order to ensure the trans-
mission of higher-priority packets. This algorithm is
used whenever more packets are supposed to be sent to
the Internet than the upstream transmission rate of the
Internet connection allows.
•As long as no packets are being sent from higher-priority
applications, the full transmission rate of the Internet
connection is available for low-priority packets.
Setting Up Prioritization in the FRITZ!Box
In order to use prioritization, the expert mode must be en-
abled in the user interface of the FRITZ!Box.
1. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “System
/ Expert Mode” menu.
2. Prioritization is set up in the “Internet / Filters / Prioriti-
zation” menu.

VPN: Remote Access to the Home Network
49
10.6 VPN: Remote Access to the Home Network
Via VPN (see glossary) a secure remote access to the network
of the FRITZ!Box can be established. The VPN solution for the
FRITZ!Box features the following:
•The VPN solution for the FRITZ!Box is based on the IPSec
standard.
•Computer-LAN coupling and LAN-LAN coupling: VPN con-
nections can be set up for individual remote computers
or even for remote networks.
•A maximum of eight simultaneous active VPN connec-
tions is supported.
•The configuration files for the VPN connections are creat-
ed using a separate program. The program is provided
free of charge and can be downloaded from the AVM web
site.
•A free VPN client for individual computers can also be
downloaded from the AVM web site.
The AVM web site offers a Service Portal which presents com-
prehensive information on VPN in general and in connection
with the FRITZ!Box. Visit this portal to obtain more detailed in-
formation.
www.avm.de/en/vpn
Setting Up VPN in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Enable the expert settings in the “System / Expert
Mode” menu.
3. Select the “Internet / Permit Access” menu.
4. Select the “VPN” page.
See the Online Help of the FRITZ!Box to set up VPN.

50
DNSSEC: Security for DNS Queries
Supplementary Software for VPN
All of the information required for a VPN is saved in a configu-
ration file. The terminals involved in any VPN must receive
this file.
If an individual computer is integrated into a network via a
VPN, the computer must have a VPN client installed.
•“Configure FRITZ!Box VPN Connection” Wizard
AVM provides the “Configure FRITZ!Box VPN” software
for creating configuration files. This program is a Wizard
that takes you step by step through the VPN configura-
tion. All of the necessary VPN settings, like the encryp-
tion method and access rules, are set automatically. The
resulting configuration files must be imported to the re-
spective terminals of the VPN tunnel. At the terminal
with the FRITZ!Box the configuration file is then imported
to the FRITZ!Box. The VPN parameters in these files can
be adjusted manually to connect to products by other
manufacturers.
•The “FRITZ!VPN” VPN Client
AVM offers the “FRITZ!VPN” software as a VPN client.
Both the Wizard and the client can be downloaded free of
charge from the VPN Service Portal on the AVM web site:
www.avm.de/en/vpn
10.7 DNSSEC: Security for DNS Queries
DNSSEC is short for Domain Name System Security Exten-
sions. As the name says, this is an extension of DNS, the do-
main name system.
DNSSEC ensures that both the DNS server and the informa-
tion returned by the DNS server are authentic, or genuine.

DNSSEC: Security for DNS Queries
51
Support with the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box supports DNSSEC queries over UDP.
The FRITZ!Box has a DNS proxy. The computers in the home
network use the FRITZ!Box as a DNS server. The FRITZ!Box for-
wards DNSSEC queries from the home network to the Inter-
net. The FRITZ!Box forwards DNSSEC responses from the In-
ternet to the home network.The DNSSEC information must be
validated on the computer in the home network. For this DNS-
SEC must be supported in the operating system.
Security with DNSSEC
When a home user surfs the web, she or he sends queries to
the Internet by entering URLs in the address line of his browser.
A URL is the name of a web site that is easy to remember, such
as avm.de/en. Every query is sent to the DNS server first. The
DNS server resolves the URL into the corresponding IP address.
There is one unambiguous IP address for every URL.
The home user relies on the authenticity of the IP address re-
turned by the DNS server. Authentic means that the response
is the IP address of the desired web site, and not a faked IP
address that leads to a fake web site. DNSSEC can ensure that
the returned addresses are authentic.

52
FRITZ!Box as a WLAN Base Station
11 FRITZ!Box as a WLAN Base Station
The FRITZ!Box supports WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) technolo-
gy. In this chapter you will learn how you can use WLAN with the
FRITZ!Box.
11.1 Security
Security is of utmost importance within radio networks.
Therefore it is important that no unauthorized users can reg-
ister in a WLAN to use its Internet access or shared network
resources.
FRITZ!Box includes settings on various levels that contribute
to the security of your WLAN and thus to the security of your
computers.
Wireless Network Name (SSID)
In the factory settings of the FRITZ!Box, the name of the wire-
less network (SSID) is set to “FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE”.
11.2 Guest Access: WLAN Connection for Guests
You can connect computers with the FRITZ!Box via WLAN so
that they can access the Internet without being integrated in
the home network of the FRITZ!Box. This function is called
“guest access”.
Your guests can use the guest access, for instance, to surf the
web with a notebook and to receive e-mail.
Radio signals can also be received outside of office or resi-
dential spaces and abused for criminal purposes.
It may occur that an additional device with the same
FRITZ!Box network name is located in the vicinity of your
FRITZ!Box. Therefore we recommend changing the preset ra-
dio network name.

Setting Up Night Service for WLAN
53
Guest Access Properties
•The guest radio network is a separate radio network with
its own name (SSID). It is independent of the wireless
network of the FRITZ!Box that integrates computers in
the home network.
•Computers connected via guest access are not part of
the home network.
•The guest network is secured with its own network key.
This network key can be changed as desired without af-
fecting the computers in your home network.
Setting Up Guest Access in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Make sure that the wireless radio network (WLAN) is en-
abled in the “WLAN / Radio Network” menu.
4. Select the menu “WLAN / Guest Access” and configure
the guest radio network. For more information, see the
Online Help of the FRITZ!Box.
11.3 Setting Up Night Service for WLAN
In the FRITZ!Box you can set up night service for the WLAN ra-
dio network. Then the FRITZ!Box switches to hibernation at
specified times and turns off the radio network. This has the
following advantages:
•reduced power consumption when idle
•time-controlled Internet access: with night service you
can ensure that your children are only allowed to surf the
web until a certain time of day
Switching Night Service for WLAN On and Off
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Select the “System / Night Service” menu.

54
Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection
3. Enable the “Use schedule for WLAN radio network” op-
tion.
4. Enable or disable the option “The radio network cannot
be switched off until no more WLAN devices are active”.
Option enabled: The radio network remains switched on
until all wireless connections between the FRITZ!Box and
other WLAN devices have been ended.
Option is disabled: The radio network is switched off im-
mediately at the start of the specified period.
5. Define the days and times at which the FRITZ!Box WLAN
radio network should be switched off.
6. Save your settings by clicking “Apply”.
Night service for WLAN is now enabled. To disable night ser-
vice, remove the checkmark in front of “Use schedule for
WLAN radio network” and click “Apply”.
Switching On WLAN during Night Service
The WLAN radio network of the FRITZ!Box can be switched
back on at any time during night service:
Press the WLAN button on the FRITZ!Box or enable the WLAN
radio network using a connected telephone (see page 120).
11.4 Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection
The range of a WLAN radio network is influenced by various
external circumstances. The following factors have an espe-
cially strong influence on the distance over which your
FRITZ!Box can establish a stable, high-throughput wireless
connection:
•the WLAN device used
•structural conditions
•the number of devices operating near the access point in
the same frequency range.
Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection
55
If needed, you can extend the range of your WLAN radio net-
work with a WLAN repeater, for instance with the FRITZ!WLAN
Repeater N/G or FRITZ!WLAN Repeater 300E from AVM. A
WLAN repeater is a supplementary device that is not included
in the FRITZ!Box package.
Instead of using a WLAN repeater, you can set up a Wireless
Distribution System. For this you need, in addition to the
FRITZ!Box, another WLAN access point that is configured as a
WDS repeater (see page 55).
Using the FRITZ!WLAN Repeater
With the FRITZ!WLAN Repeater N/G from AVM you can extend
the range of your WLAN radio network quickly and easily, for
instance to overcome structural conditions that are character-
ized by thick materials and heavy shielding. The FRITZ!WLAN
Repeater N/G supports all common WLAN standards, is espe-
cially easy to install and can be operated at any 230-V power
outlet. For more information on the FRITZ!WLAN Repeater
N/G, see the web site at:
www.avm.de/en/Produkte/FRITZ_WLAN/FRITZ_WLAN_
Repeater_N_G
Setting Up a WDS
To use WDS (Wireless Distribution System) to increase the
range of your WLAN radio network, you need another WLAN
base station in addition to the FRITZ!Box. This can be a sec-
ond FRITZ!Box or any other WLAN base station that supports
WDS. The first WLAN base station then works as a WDS base
station and the second as a WDS repeater.
The WDS base station and WDS repeater are connected to
each other via WLAN. The WDS base station then can use the
WDS repeater to reach even computers that are outside its
own range, but within the range of the WDS repeater.

56
Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection
WDS: Expanding the WLAN range using a WDS repeater
Note the following for WDS configuration:
•To expand the range of your wireless network, you need
at least one additional WLAN base station. The wireless
network of your FRITZ!Box can be expanded to a WDS
(Wireless Distribution System) with up to three WLAN
base stations.
•All WLAN base stations implemented in the WDS must
support WDS and be configured for this technology.
•All WLAN base stations implemented as repeaters in the
WDS must be located within the radio range of the WDS
base station.
•The FRITZ!Box can function as a WDS base station to es-
tablish the Internet connection for other WDS repeaters,
or as a WDS repeater to expand the range of a WDS base
station.
•All WDS connections between the WDS base station
and the WDS repeaters must be secured using the
same encryption (e.g. WPA/WPA2). Note that the WPA2
encryption method is available only when your network
consists of AVM devices, since in the WLAN standard on-
ly WEP encryption has been specified for WDS connec-
tions.
•All WLAN base stations in the WDS must use the same
radio channel.
FRITZ!Box (Base station)Repeater
Power
supply
P
s
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Phone
Powe
Powe
Powe
Powe
Powe
r/
r/
r/
r/
r/ LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
LTE
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
DECT
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
WLAN
Info
I
I
I
Inf o
nfo
nfo
nfo

WLAN Standards
57
•Every WLAN base station participating in the WDS fulfills
the tasks of a WLAN access point for its WLAN clients.
This means that the WLAN clients see each WLAN base
station with an individual name (SSID) and individual
encryption settings.
If you use the WLAN control software provided in
Windows 7, Windows Vista or by the Windows XP Service
Pack 2 on your WLAN clients, you can assign the same
SSID and the same encryption settings to different WLAN
base stations. Each client can then automatically register
at the WLAN base station with the best availability.
•Each IP address may be assigned only once in the wire-
less network.
11.5 WLAN Standards
The WLAN standards IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b,
IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n and IEEE 802.11i were devel-
oped by the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
(IEEE).
The IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and
IEEE 802.11n standards define the throughput within a wire-
less radio network. IEEE 802.11i is a security standard.
Standards for the Throughput Rate
Data Throughput
The throughputs listed differentiate between gross and net
transmission rates. The net speed describes the transmission
rate of the user data.
The FRITZ!Box supports your choice of the standards
IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.11n.
WLAN devices based on one or more of the standards listed
can be used for WLAN connections with the FRITZ!Box.

58
WLAN Standards
The standards are intended for different frequency bands.
IEEE 802.11a
Because this standard works exclusively in the seldom used
5-GHz range, it offers the opportunity to transmit data rela-
tively free of interference from external influences. WLAN de-
vices that support 802.11a are much less common than de-
vices that work in accordance with the 802.11b/g standard.
IEEE 802.11b
With a maximum throughput rate of 11 Mbit/s, this is the old-
est WLAN standard. Older WLAN devices of the first genera-
tion can communicate with the FRITZ!Box using 802.11b.
However, if the WLAN device supports newer standards such
as 802.11g, the latest standard should be used.
IEEE 802.11g
This is currently the most common WLAN standard. It commu-
nicates with a maximum of 54 Mbit/s gross in the 2.4-GHz
frequency range (ISM) and guarantees broad compatibility
with many WLAN devices.
However, due to heavy use of the 2.4-GHz range, interference
is more common than in the less-used 5-GHz range.
IEEE 802.11n
This standard allows for high throughput rates and ranges.
The FRITZ!Box supports 802.11n in the 2.4-GHz frequency
band, or, if desired, also in the 5-GHz frequency band. Modu-
lation processes and antenna techniques like MIMO (Multiple
Input, Multiple Output) use whichever frequency band is
available more effectively than the older standards.
Standard Frequency Band
Gross Data Throughput up to
Net Data Throughput up to
802.11b 2.4 GHz 11 Mbit/s 5 Mbit/s
802.11g 2.4 GHz 54 Mbit/s 25 Mbit/s
802.11a 5 GHz 54 Mbit/s 25 Mbit/s
802.11n 2.4 / 5 GHz 300 Mbit/s 150 Mbit/s

WLAN Standards
59
Thanks to compatibility with the 802.11g standard, you can
also continue to use older WLAN devices.
Setting the Right Standard in the FRITZ!Box
The throughput rate that can be achieved in your WLAN radio
network depends on the WLAN standards used by the inte-
grated WLAN devices. These WLAN standards must also be
set in the FRITZ!Box. Proceed as follows to check which WLAN
standards are set and change them if needed:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Open the “WLAN / Radio Channel” menu and select “Ad-
just radio channel settings” to make the desired changes.
•In order to communicate with each other, the FRITZ!Box
and all WLAN devices must work in the same frequency
band.
•The standard you configure in the FRITZ!Box must be
compatible with the standards of all WLAN devices used
in the WLAN.
Make a note of which standards the WLAN devices in your
network are compatible with and then adjust the FRITZ!Box
settings according to the following information:
The use of the 802.11n standard—and thus the availability
of higher throughput rates—is possible only if the WLAN con-
nection is secured using the WPA2 security mechanism (AES-
CCMP).
Note the following for the configuration of this setting:

60
WLAN Standards
•Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or both of the following stan-
dards:
802.11n
802.11g
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11n+g
The 2.4-GHz frequency band will be used.
•Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or both of the following stan-
dards:
802.11b
802.11g
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11b+g
The 2.4-GHz frequency band will be used.
•Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or several of the following stan-
dards:
802.11n
802.11g
802.11b
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11n+g+b
The 2.4-GHz frequency band will be used.

WLAN Standards
61
•Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or both of the following stan-
dards:
802.11n
802.11a
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11n+a
The 5-GHz frequency band will be used.
The Standard for Security
IEEE 802.11i
The WPA2 security mechanism is defined in the IEEE 802.11i
standard. WPA2 is an extension of the familiar security mech-
anism WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access).
The main feature of the extension of WPA to WPA2 is the AES-
CCMP encryption process.
FRITZ!Box supports the AES encryption procedure as part of
the WPA2 mechanism, and the TKIP encryption procedure as
part of the WPA mechanism. This means that the FRITZ!Box
can be used in combination with any WLAN devices that also
support WPA2 with AES or WPA with TKIP.
Mechanism Encryption
WPA TKIP (Temporary Key Integrity Protocol)
WPA2 TKIP
AES-CCMP
based on the extremely secure AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) procedure. CCMP (Coun-
ter Mode with CBC-MAC Protocol) defines how
the AES procedure is applied to WLAN pack-
ets.

62
Frequency Ranges
11.6 Frequency Ranges
WLAN uses the frequency ranges at 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz as its
transmission range.
With the FRITZ!Box you can establish WLAN connections in ei-
ther the 2.4-GHz or the 5-GHz frequency range.
2.4-GHz Frequency Band
In the 2.4-GHz frequency band WLAN works in the same range
as Bluetooth, microwave devices and various other devices
like radio-controlled toys, garage-door openers and video
bridges. This means that interference may occur within
WLANs operated in the vicinity of such devices. Generally this
has adverse effects on the transmission rate, including abort-
ed connections.
In the 2.4-GHz frequency range the European regulation au-
thorities have designated 13 channels for WLAN. A channel
can have a bandwidth of 20 MHz (throughput up to
130 Mbit/s) or 40 MHz (throughput of up to 300 Mbit/s).
Channels located directly next to each other in the 2.4-GHz
band may overlap and result in mutual interference. For in-
stance, if several WLANs are operated close to each other in
the 2.4-GHz frequency range with a bandwidth of 20 MHz, a
distance of at least five channels should be left empty be-
tween each two channels used. This means that if channel 1
is selected for one WLAN, the channels 6 through 13 can be
selected for a second WLAN. This maintains the minimum dis-
tance between channels.
Should interference in a WLAN persist, the first step should
be to select a different channel.
WLAN Autochannel
With the WLAN autochannel function, the FRITZ!Box automati-
cally searches for the channel subject to the least interfer-
ence. This process takes into consideration interference from
radio networks in the vicinity (WLAN base stations) and po-
tential sources of interference (for instance video bridges,

Frequency Ranges
63
baby monitors, microwave ovens). Should problems with in-
terference persist despite this function, try to identify the
source of interference and switch it off manually.
Additional tips on interference in the WLAN radio network are
presented in the section Ruling Out Interference Caused by
Other Wireless Networks from page 118.
5-GHz frequency band
The FRITZ!Box can operate in the 5-GHz frequency band as an
alternative. This frequency range is used much less often
than the most common 2.4-GHz frequency range.
In the 5-GHz frequency band the FRITZ!Box supports automat-
ic channel switching by DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection).
DFS ensures that the channels from 52 to 140 are kept free
for higher priority users, like weather radar systems. If you are
operating your FRITZ!Box in one of these channels, it moni-
tors the selected channel periodically for higher priority us-
ers, and, if necessary, switches to a different channel. Note
that the FRITZ!Box waits up to ten minutes, as legally re-
quired, before occupying a free channel. During this period
you cannot register any WLAN devices. The WLAN connection
is then established automatically. For more information, see
the section Avoiding WLAN Channels with DFS on page 117.
A prerequisite for use of the 5-GHz frequency band is that all
WLAN devices in the network support this frequency range in
accordance with the IEEE 802.11a or IEEE 8002.11n stan-
dard.
2.4 GHz or 5 GHz
The FRITZ!Box works in the wireless network either in the 2.4-
GHz range or in the 5-GHz range, but not parallel in both fre-
quency ranges at the same time.
Bandwidth
In both frequency ranges you can select between channel
bandwidths of 20 MHz or 40 MHz (exception: channel 140 in
the 5-GHz frequency band). The FRITZ!Box initially attempts
to select a channel with 40 MHz bandwidth (throughput up to
300 Mbit/s). If this is not possible due to interference or

64
Frequency Ranges
channels already being used by other WLANs in the vicinity,
the FRITZ!Box automatically switches temporarily to a chan-
nel with 20 MHz bandwidth. Greater bandwidth provides for
higher data throughput:
Increasing bandwidths also increases the probability of inter-
ference by wireless networks in the vicinity. Large bandwidths
reduce the frequency range available to other wireless net-
works in the vicinity.
Allocation of the WLAN Channels in the 2.4-GHz Range
Allocation of the WLAN Channels in the 5-GHz Range
Bandwidth (MHz) Maximum Data Throughput (Mbit/s)
20 130
40 300
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
1 2.412 8 2.447
2 2.417 9 2.452
3 2.422 10 2.457
4 2.427 11 2.462
5 2.432 12 2.467
6 2.437 13 2.472
7 2.442
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
36 5.18 108 5.54
40 5.20 112 5.56
44 5.22 116 5.58
48 5.24 120 5.60
52 5.26 124 5.62
56 5.28 128 5.64
60 5.30 132 5.66
64 5.32 136 5.68
100 5.50 140 5.70 (20 MHz bandwidth only)
104 5.52

FRITZ!Box as a Telephone System
65
12 FRITZ!Box as a Telephone System
The FRITZ!Box is a telephone system (or PBX: Private Branch Ex-
change) for Internet telephony. This chapter describes convenience
functions for the telephone system that can be configured in the
FRITZ!Box user interface, for instance telephone books, answering
machines and call diversion.
You will also find out which convenience functions can be used to
make calls, for instance internal calling, alternating between calls,
fowarding calls and three-party conferences.
12.1 Using the Telephone Book and Call List
Telephone Book
A telephone book is at your disposal in the FRITZ!Box. In the
user interface the FRITZ!Box telephone book is found in the
“Telephony” menu.
If a cordless telephone from AVM (for instance FRITZ!Fon MT-
F) is registered on the FRITZ!Box, you can use the telephone
book directly on the cordless telephone. If multiple AVM cord-
less telephones are registered, you can set up an individual
telephone book for each cordless telephone in the FRITZ!Box.
Call List
In the call list the FRITZ!Box saves outgoing and incoming
calls, missed calls, and sent and received faxes.
In the FRITZ!Box user interface the call list is found in the “Te-
lephony” menu.
If the number of a caller or someone called is entered in the
FRITZ!Box telephone book, the call list will display the name
from the telephone book.
Numbers that are not saved in the telephone book can be
added to the telephone book from the call list.
The call list can be stored as a CSV file. CSV files can be
opened in programs like spreadsheet software.

66
Setting Up the FRITZ!Box Answering Machine
12.2 Setting Up the FRITZ!Box Answering Machine
You can configure up to five different answering machines in
the FRITZ!Box.
Enable an Answering Machine
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Select “Telephony / Telephony Devices”.
3. Click “Configure New Device”.
4. Under “Integrated in the FRITZ!Box”, select the “Answer-
ing machine” option and confirm by clicking “Next”.
5. Specify the mode, greeting delay and greeting length. (In
the “Greeting only” mode, callers will hear a recording,
but cannot leave any message for you.)
6. Enter a name for the answering machine and confirm by
clicking “Next”.
7. Specify which calls the answering machine should ac-
cept. Select one or multiple telephone numbers and
confirm by clicking “Next”.
8. Check the settings of the answering machine and then
click “Apply”.
Now the answering machine is enabled.
Switching the Answering Machine On or Off
All configured answering machines are displayed in the
FRITZ!Box user interface under “Telephony / Telephony Devic-
es”. Here you can disable or delete answering machines and
enable additional functions.
For instance, you can enable the “Send messages via e-mail”
setting for each answering machine. Messages callers leave
on the answering machine then will be sent to you by e-mail.
You can select any e-mail address you want. The messages
are sent as audio files.
Setting Up the FRITZ!Box Answering Machine
67
Picking Up a Call from the Answering Machine
With this function, calls that have already been answered by
an answering machine can be transferred to your telephone:
Operating the Answering Machine Using the Voice Menu
The answering machines of the FRITZ!Box can be operated us-
ing a voice menu. You can listen to new messages, for in-
stance, or switch the answering machine on and off.
Picking Up a Call
NPick up the handset.
s09 Dial the sequence shown at left.
PThe call is now connected to your extension, and
you can talk with the caller.
Operating the Answering Machine Using the Voice Menu
NPick up the handset.
ss600
ss601
ss602
ss603
ss604
Select:
Answering machine 1
Answering machine 2
Answering machine 3
Answering machine 4
Answering machine 5
You will enter the voice menu of the answering ma-
chine.
Follow the voice menu.
If you do not want to wait for the voice menu instruc-
tions, you can press a telephone key right away.

68
Setting Up the FRITZ!Box Answering Machine
The Answering Machine Menu
Main menu
1Play back messages
If no messages are available, you will hear two short audio sig-
nals and return to the main menu.
1Play back messages
3Call back the caller of the message
5Delete message
7To previous message
9To next message
0Listen to “Play back messages” menu again
rBack to main menu
2Delete all messages
3Switch answering machine on/off
4Record greetings
1Record greeting message
2Record announcement
3Record closing announcement
Record and select
1Listen to all greetings/announcements of the select-
ed type > Select the desired recording by pressing 2
5Delete greeting/announcement
8Record greeting/announcement > End recording by
pressing 1
0Listen to “Record and Select” menu again
rBack to main menu
0Listen to “Record greetings” menu again
rBack to main menu
5Switch recording and directions mode on/off
0Listen to main menu again

Setting Up FRITZ!Box Fax Reception
69
12.3 Setting Up FRITZ!Box Fax Reception
With the FRITZ!Box you can receive faxes without having to
connect a fax machine. The FRITZ!Box automatically forwards
incoming faxes by e-mail or saves the faxes on a connected
USB storage medium.
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 30).
2. Select the “Telephony / Telephony Devices” menu.
3. Click “Configure New Device”.
4. Select the “Fax reception” option and confirm by click-
ing “Next”.
5. Enter a fax ID. This could be your fax number or name, for
instance.
6. Define whether the FRITZ!Box forwards incoming faxes
by e-mail or saves them.
If you would like to enter multiple e-mail addresses, sep-
arate the addresses with commas.
7. Confirm with “Next”.
8. Select one or multiple telephone numbers you would
like to use exclusively for fax reception.
9. Confirm by clicking “Next” and “Apply”.
Sending Faxes with FRITZ!fax for FRITZ!Box
To send faxes you can install the free “FRITZ!fax for FRITZ!Box”
software. This program is available at www.avm.de/en (for
Windows 7, Vista and XP).
12.4 Setting Up Call Diversion
You can configure call diversion settings in the FRITZ!Box. Call
diversion forwards incoming telephone calls, for instance, to
an external telephone number.
Termékspecifikációk
| Márka: | AVM |
| Kategória: | router |
| Modell: | FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE International |
Szüksége van segítségre?
Ha segítségre van szüksége AVM FRITZ!Box 6840 LTE International, tegyen fel kérdést alább, és más felhasználók válaszolnak Önnek
Útmutatók router AVM

30 Március 2025

9 December 2024

6 December 2024

5 Október 2024

27 Szeptember 2024

23 Augusztus 2024

22 Augusztus 2024

22 Augusztus 2024

22 Augusztus 2024

22 Augusztus 2024
Útmutatók router
- router Samsung
- router Acer
- router Milwaukee
- router Bosch
- router AEG
- router StarTech.com
- router Einhell
- router Nokia
- router HP
- router Makita
- router BenQ
- router Apple
- router Ubiquiti Networks
- router Siemens
- router TP-Link
- router Medion
- router Motorola
- router Vimar
- router LogiLink
- router Alcatel
- router Roland
- router TCL
- router Digitus
- router Zebra
- router Xiaomi
- router TRENDnet
- router Mercusys
- router EZVIZ
- router Dell
- router Lancom
- router Strong
- router Gigabyte
- router Conceptronic
- router Thomson
- router Juniper
- router Kyocera
- router Hikvision
- router Keewifi
- router Vivanco
- router Netgear
- router Huawei
- router Asus
- router Vtech
- router Hama
- router Zoom
- router Renkforce
- router Synology
- router Draytek
- router Iogear
- router Güde
- router Hitachi
- router Mikrotik
- router Toolcraft
- router ZyXEL
- router SPL
- router Dahua Technology
- router Smart-AVI
- router Black & Decker
- router Devolo
- router Planet
- router Tenda
- router BT
- router Black Box
- router MSI
- router Gembird
- router Cisco
- router PowerPlus
- router ATen
- router Google
- router Metabo
- router Bea-fon
- router ZTE
- router Edimax
- router Vodafone
- router ModeCom
- router HiKOKI
- router Foscam
- router Milan
- router Manhattan
- router Kogan
- router Festool
- router EnGenius
- router Sigma
- router Western Digital
- router D-Link
- router Media-Tech
- router Blustream
- router Milesight
- router Moxa
- router Sagem
- router Razer
- router Trust
- router Porter-Cable
- router Konig
- router Alfa
- router MuxLab
- router DeWalt
- router AVMATRIX
- router IFM
- router A-NeuVideo
- router Atlona
- router Schneider
- router AJA
- router Lindy
- router Cudy
- router Barco
- router QNAP
- router NEC
- router Silverline
- router Cotech
- router Siig
- router Gefen
- router Kathrein
- router Avenview
- router Lantronix
- router Technicolor
- router FSR
- router Topcom
- router Holzmann
- router Arris
- router Anker
- router I-TEC
- router Keenetic
- router Linksys
- router Teltonika
- router Sitecom
- router Intelix
- router Comprehensive
- router Ocean Matrix
- router Digitalinx
- router Alfatron
- router Belkin
- router RGBlink
- router Kopul
- router KanexPro
- router Key Digital
- router Kramer
- router BZBGear
- router UPC
- router Allnet
- router Allied Telesis
- router Airlive
- router Actiontec
- router Proximus
- router Skil
- router Eminent
- router Nilox
- router Sonos
- router Patton
- router Techly
- router Totolink
- router KPN
- router Netis
- router Envivo
- router Buffalo
- router Nest
- router LevelOne
- router ICIDU
- router Clas Ohlson
- router AT&T
- router Sweex
- router Aruba
- router Phicomm
- router Kasda
- router Jung
- router Digi
- router Verizon
- router Billion
- router T-Mobile
- router RAVPower
- router Hawking Technologies
- router Nexxt
- router Beafon
- router Kraun
- router LTS
- router Zolid
- router Sagemcom
- router Telstra
- router Eero
- router Advantech
- router Mercku
- router Hercules
- router Xantech
- router Intellinet
- router Arcadyan
- router Digiconnect
- router Ubee
- router SMC
- router Tele 2
- router Peak
- router CradlePoint
- router Davolink
- router Sixnet
- router 7inova
- router AVPro Edge
- router F-Secure
- router Rosewill
- router Digicom
- router Sabrent
- router On Networks
- router PENTAGRAM
- router Leoxsys
- router Readynet
- router OneAccess
- router Accelerated
- router Nexaira
- router Hamlet
- router Approx
- router T-com
- router Amped Wireless
- router Cambium Networks
- router 3Com
- router WyreStorm
- router Ruckus Wireless
- router Dovado
- router Mach Power
- router EXSYS
- router NetComm
- router Comtrend
- router Premiertek
- router GL.iNet
- router Shinybow
- router Edgewater
- router Atlantis Land
- router Lumantek
- router Starlink
- router PulseAudio
- router Predator
- router Evolution
- router Luxul
- router StarIink
- router Silentwind
- router Keezel
- router United Telecom
- router Wisetiger
Legújabb útmutatók router

9 Április 2025

9 Április 2025

9 Április 2025

31 Március 2025

30 Március 2025

30 Március 2025

30 Március 2025

30 Március 2025

23 Március 2025

15 Január 2025